ESPrtk is a small circuit board used to transmit wireless GNSS data in high precision positioning applications.
ESPrtk is geared towards the ability to use high quality, independent, wireless and low cost platforms.
ESPrtk’s heart is a powerful ESP32 processor.
What does ESPrtk include?
ESPrtk is an abbreviation for ESP32 RTK.
ESPrtk is available in two formats. Software for DIY users and hardware for direct users.
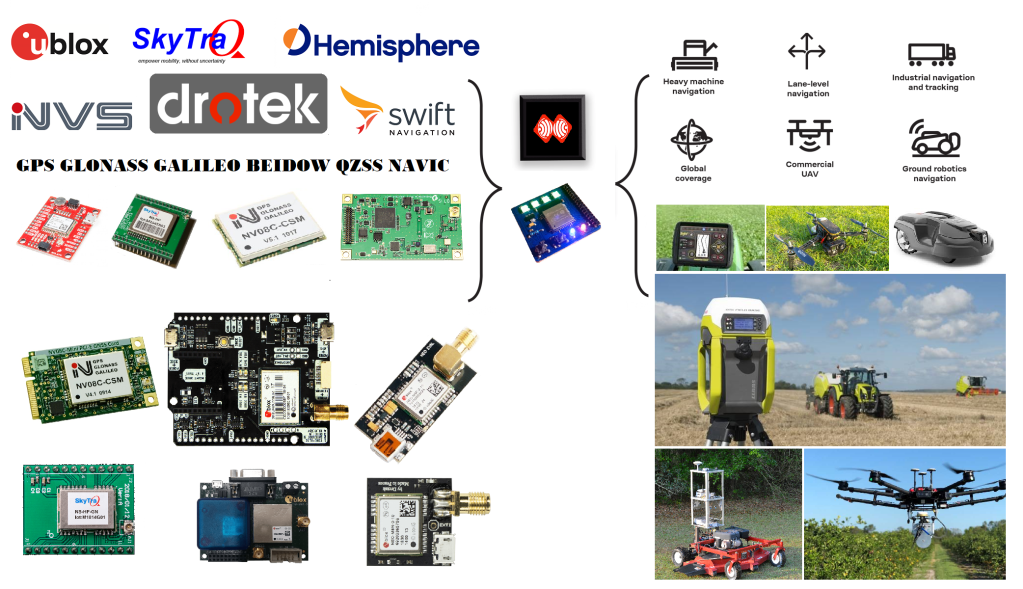
ESPrtk can be used with many GNSS RTK devices.
RTK-capable receivers require precisely calibrated antennas to process signals transmitted by the GNSS satellites. The process for achieving centimeter-level position accuracy in GNSS involves a complex algorithm known as real time kinematic (RTK) processing. In addition, they must receive and process corrections data from a ground network of GNSS receivers. These factors made traditional RTK-capable receivers costly (in excess of $5000 or even $10,000 ) and bulky, making them unsuitable for cost- and size-sensitive applications.
Recently, GNSS equipment manufacturers have started advertising inexpensive (less than $500) and compact RTK-capable receivers. Some prominent names:
- Hemisphere- Eclipse P307 (L1/L2).
- NVS Technologies- NV08C-RTK (L1).
- Swift – Piksi Multi (L1/L2).
- u-blox -NEO-M8P (L1).
- Skytraq -S2525F8 (L1).
|
Evaluation of Low-Cost, Centimeter-Level Accuracy OEM GNSS Receivers. |
RTK receivers are getting smaller and smaller, but accuracy is improving. At the same time, there was a powerful embedded CHIP is ESP32, which attracted everyone in IoT applications and GNSS data transmission for RTK positioning is one of them.
This is the best time to promote RTK.
ESPrtk aims to be simple, user-friendly and safe to use.
ESPrtk was born to provide High quality RTK positioning solution with low cost option. This is an effort to make accessing and using high-precision positioning technology easier for everyone. Especially for those who have hobby about it.
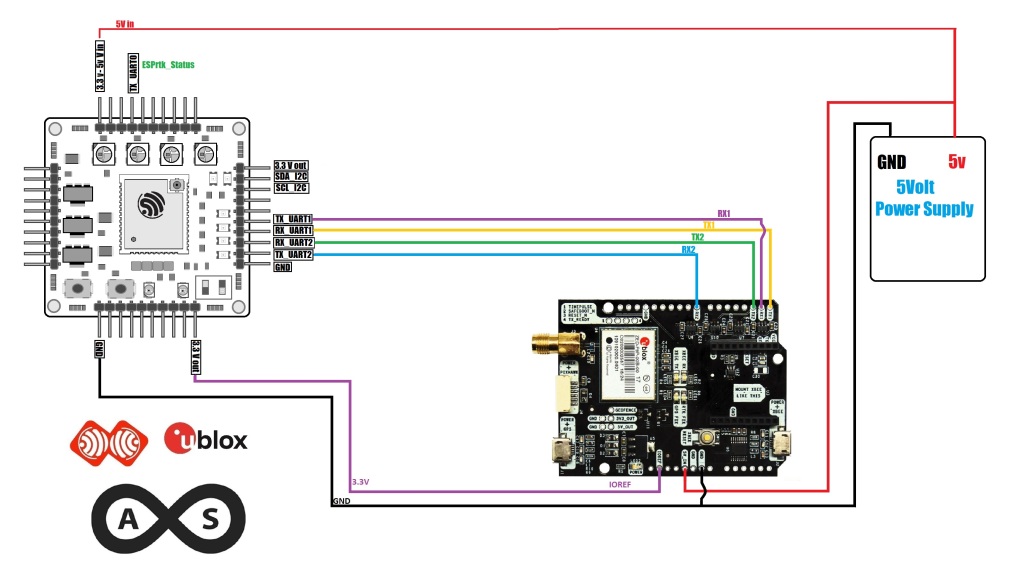
Wired connections for extremely simple use will make things faster.
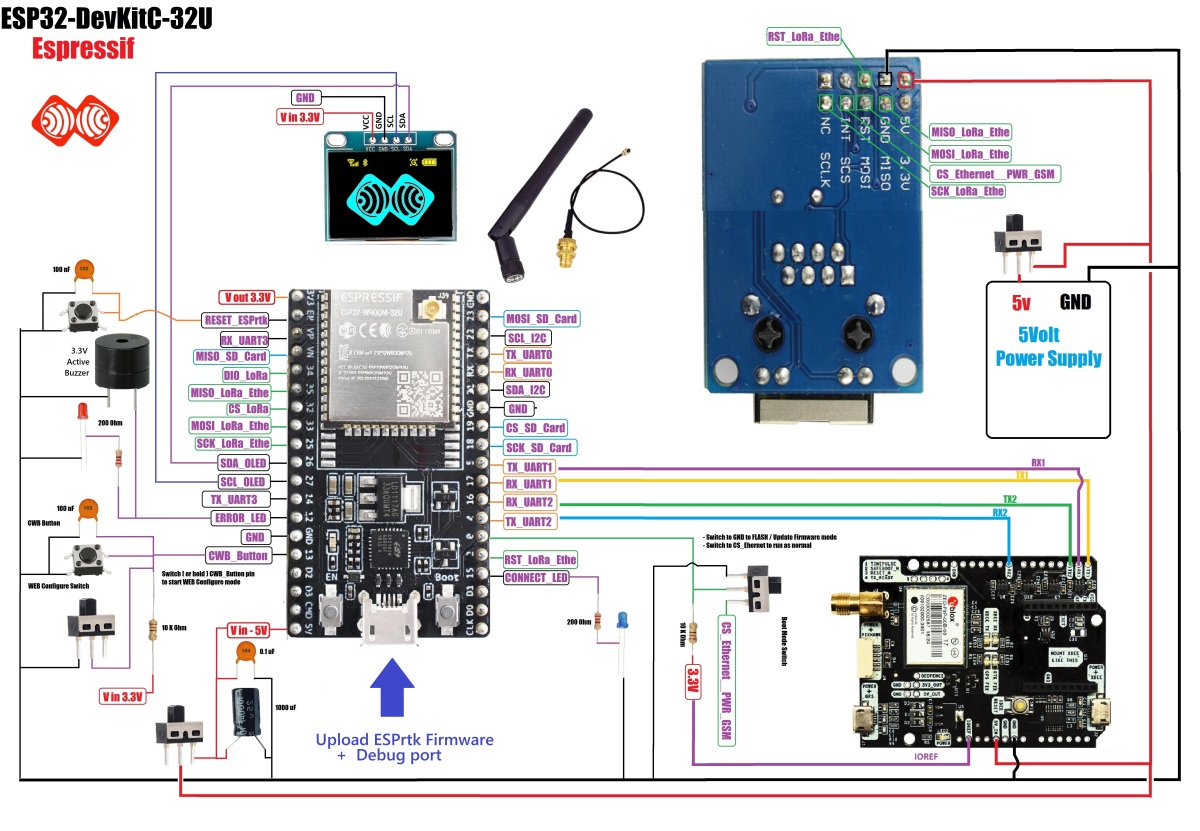
(More circuit diagram, click here)
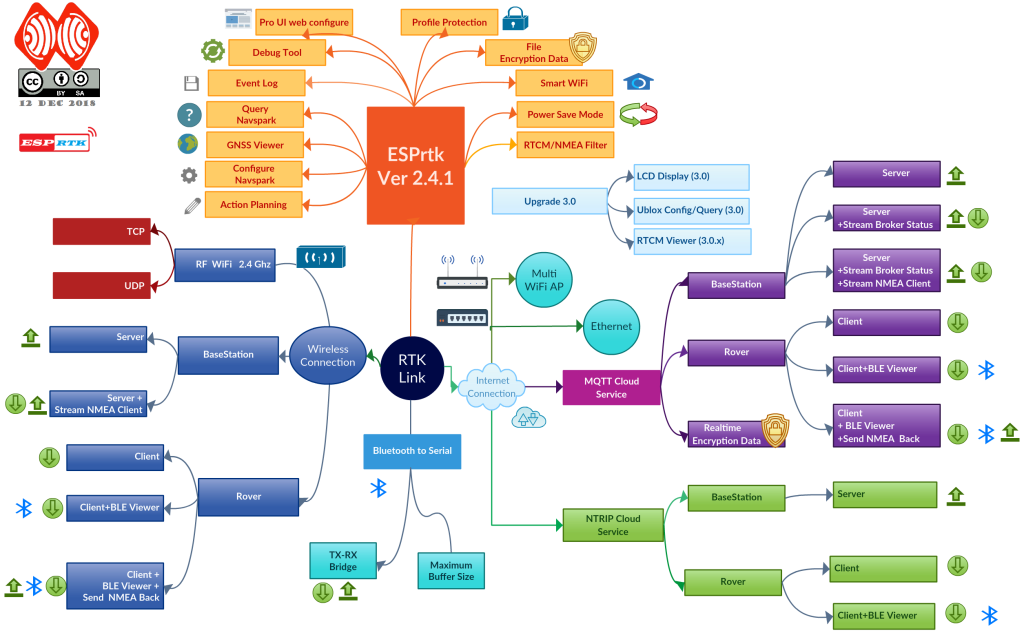
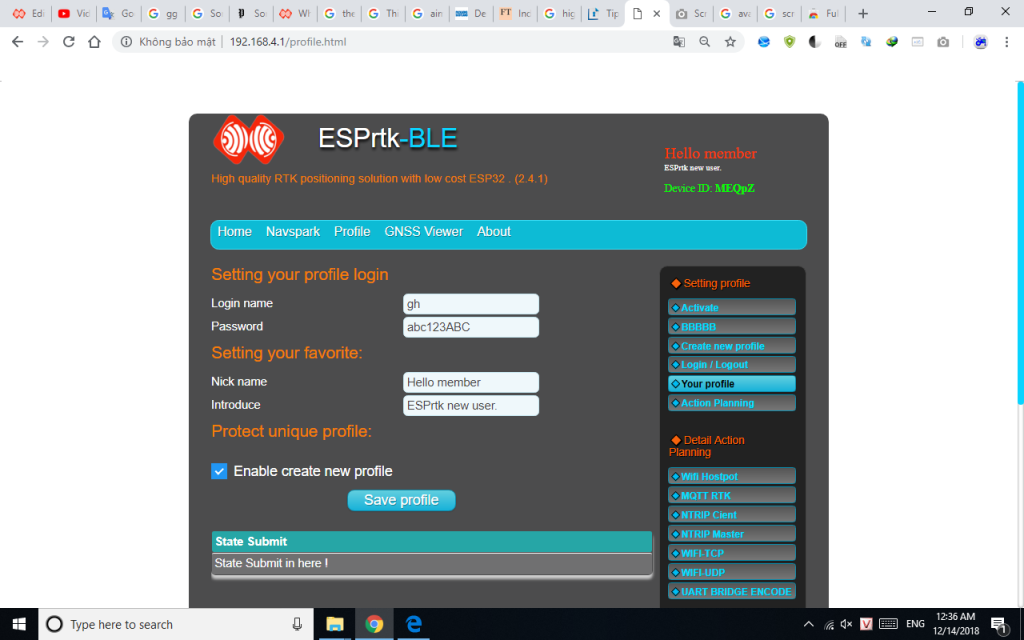
Highlights of the design are the Web Config User Interface (UI) application, which makes it easy to test or configure it and the peripherals it connects to.
Along with that are layers of security with high-level encryption for transmitting GNSS data to public servers (where your data can be abused without your permission). Data encryption is also applied to all important files on ESPrtk in order to protect users as much as possible. Users can even activate a permanent lock with their password to make sure no one can change anything on their ESPrtk.
(More circuit diagram, click here)
Support Bluetooth ,WIFI , Ethernet and GSM/2G/3G/4G/LTE connection.
You do not need to purchase HC05 module for wireless connections, ESPrtk also supports bluetooth and can use it in “UART + Bluetooth 2 ways bridge (Transmiter + Receiver)“ mode with just one quick setting.
High-speed wireless WIFI connection on ESP32 helps mobile connections for flexible Rover devices.
Ethernet connection will be suitable for Basestation with absolute stability.
Both of them are supported on ESPrtk.
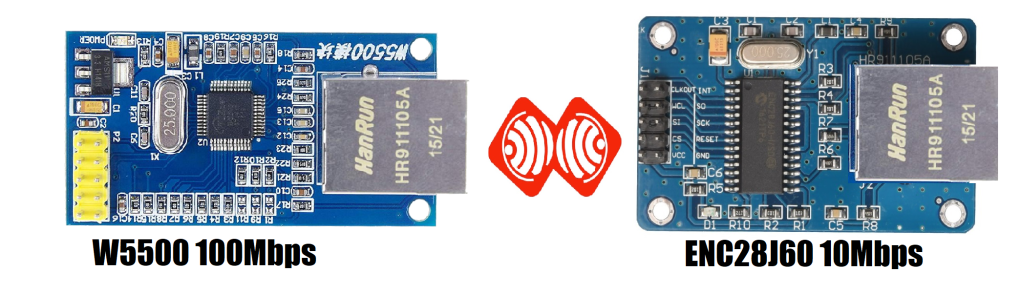
Ethernet module support is W5XX (W5500 (100Mbps) -W5100-W5200) and ENC28J60 (10Mbps) , communicate to ESPrtk via SPI port to access internet.
(More circuit diagram, click here)
Darren Lobb's BaseStation (ESPrtk + F9P) system on with several months of continuous uptime without problems.
(More circuit diagram, click here)
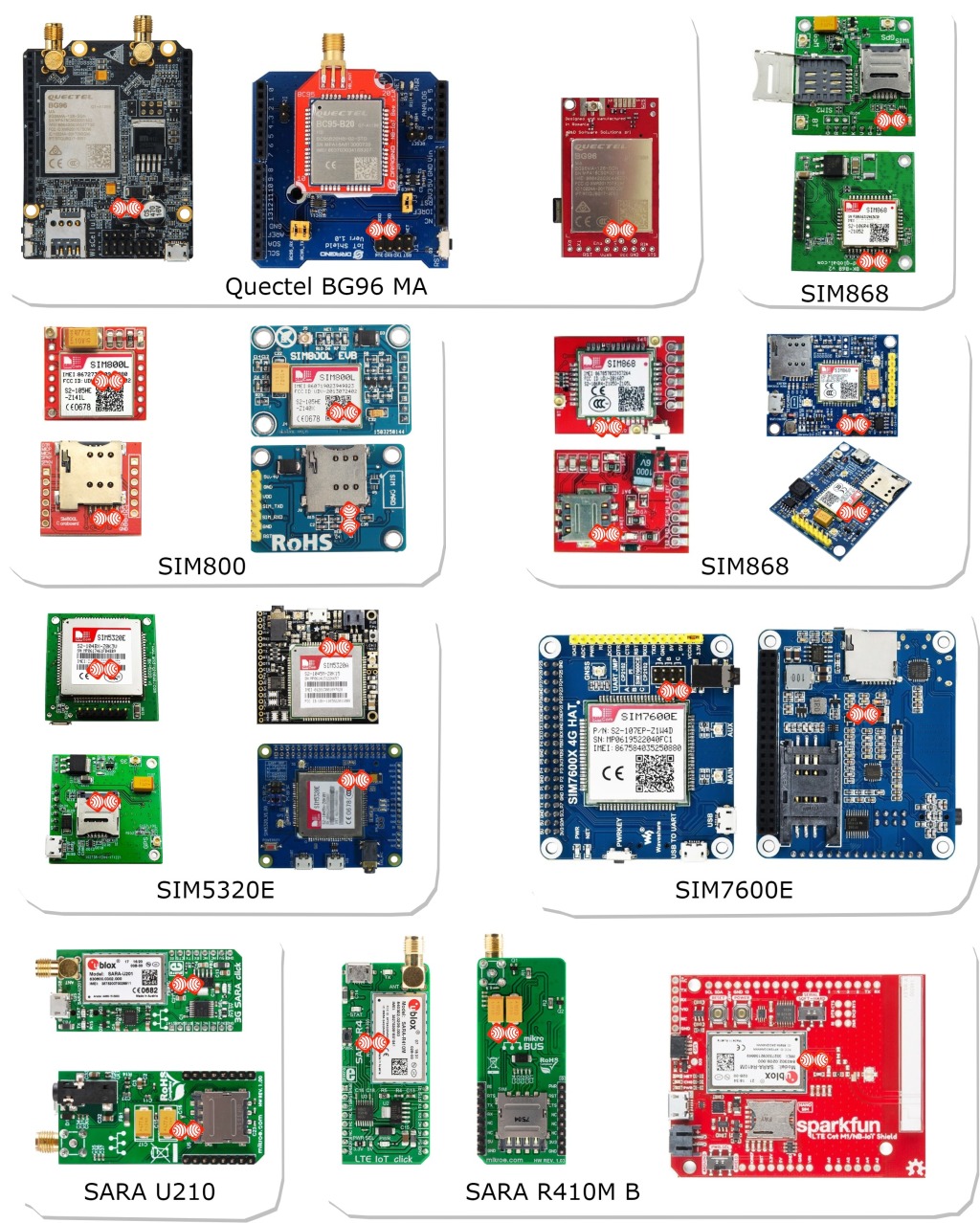
One of the important features available on version 3.9.x is Internet access by Cellular / GSM 2G 3G 4G LTE module.
The Ublox-Quectel-SIMCOM-Digital brands have good products and ESPrtk supports most of them.
From early 2020 and it takes 9 months to plan, develop and test all of these product lines to find the most suitable models.
They are: "SIM800", "SIM808-SIM868", "SIM900-SIM968-SIM968","SIM7000E", "SIM5320E-SIM5360", "SIM7100", "SIM7600E", "Ublox LEON-G100", "Ublox LISA-U2xx", "Ublox SARA-G3xx", "Ublox TOBY-L2xx", "Ublox LARA- R2xx "," Ublox MPCI-L2xx ","Ublox SARA-U2xx", "Ublox SARA-R4xx", "Ublox SARA-N4xx", "Quectel BG96", "Quectel M95", "Quectel MC60", "Digi XBee", "SequansMonarch".
Stream manager.
The supported streams on version 3.9.x are RTCM / NMEA / UBX / SKYTRAQ.
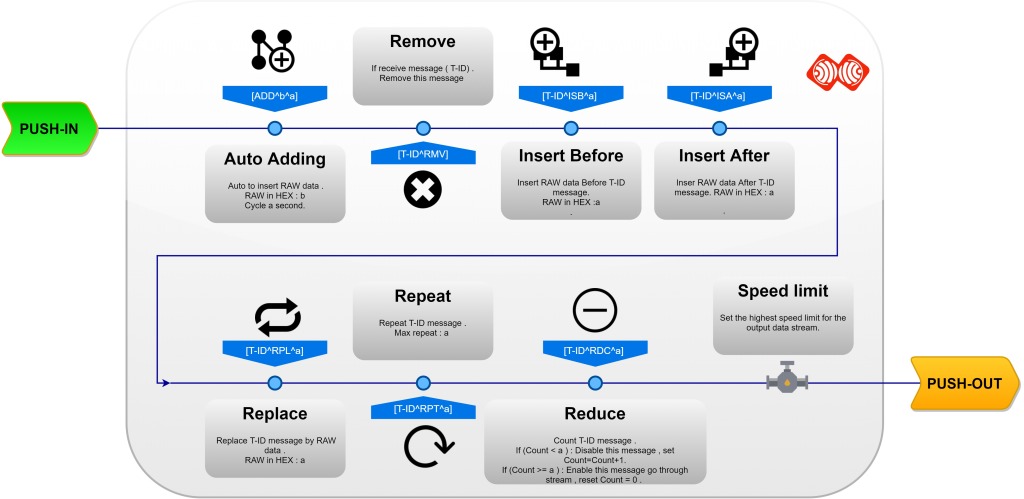
ESPrtk also allows the user to configure filters to manage the RTK data stream running through it. Can insert data, remove a message, repeat a message, replace a message with other data, minimize the appearance of a message ... and set a speed limit (highest ) for Push-Out data .
U-Center and GNSSViewer inside.
Well, you don’t need to bring your computer to configure Ublox modules or Navspark either because both of these functions have been integrated on the WEB Configure of ESPrtk. They are also designed with the same interface as the original version of U-Center and GNSSViewer to bring a feeling similar to when using software on a computer.
Both of these functions are supported with full of important features and the latest protocol for modules such as M8P, F9P, LEA, NEO .. of Ublox and NS-HP-xx, INS 3D, .. of Navspark.
(More circuit diagram, click here)
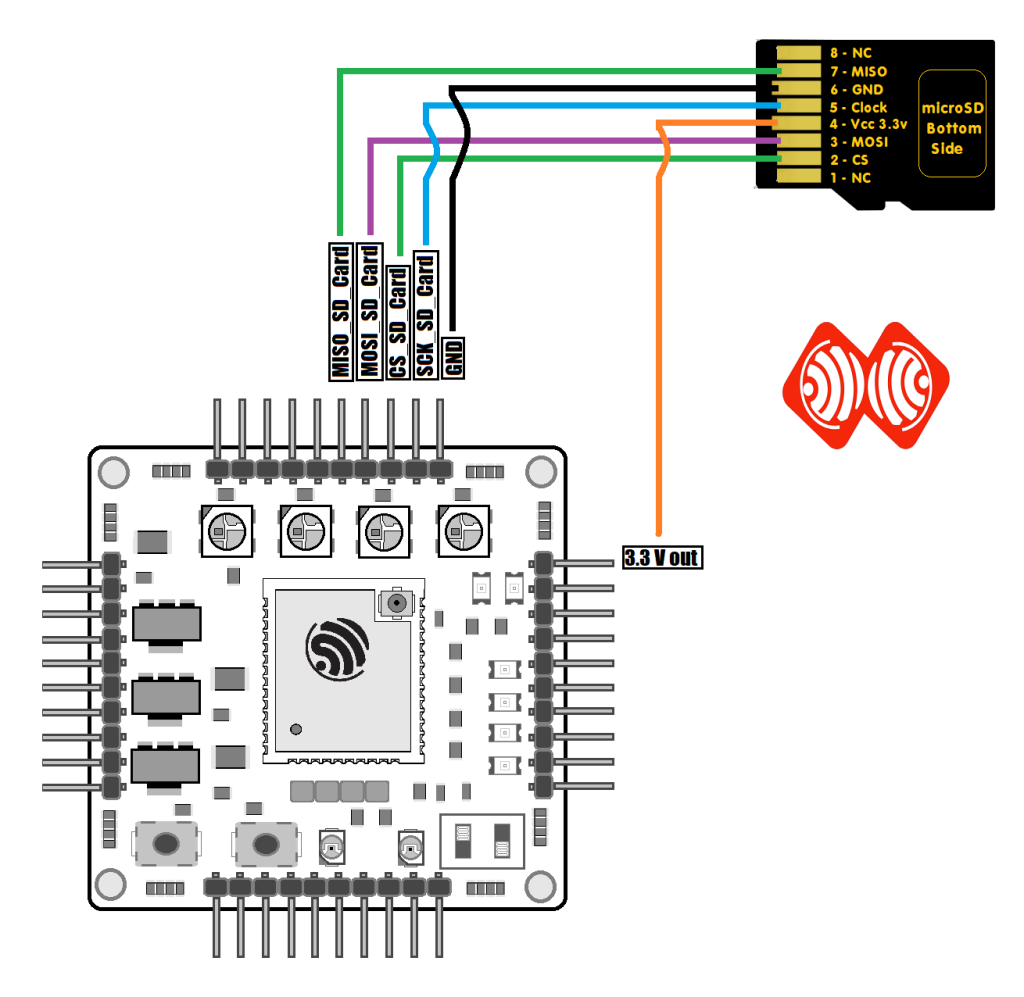
SD Card to Log NMEA/RTCM data.
When activated, ESPrtk will collect NMEA sentences from RX_UART1 port and save it to the SD card as a text file (or log file). Users can then use those files for surveying and evaluating positioning.
NMEA Logger on ESPrtk supports a variety of file formats, update cycles, NMEA filters, recording styles, etc.
This function is integrated on the Rover (Client) and all connections such as NTRIP – MQTT – WIFI TCP-WIFI UDP.
(More circuit diagram, click here)
OLED Display or Neopixel Strip.
Besides displaying status by Neopixel and LED.
Since 2.7.0 ESPrtk OLED has been integrated to provide more information and operational status of ESPrtk.
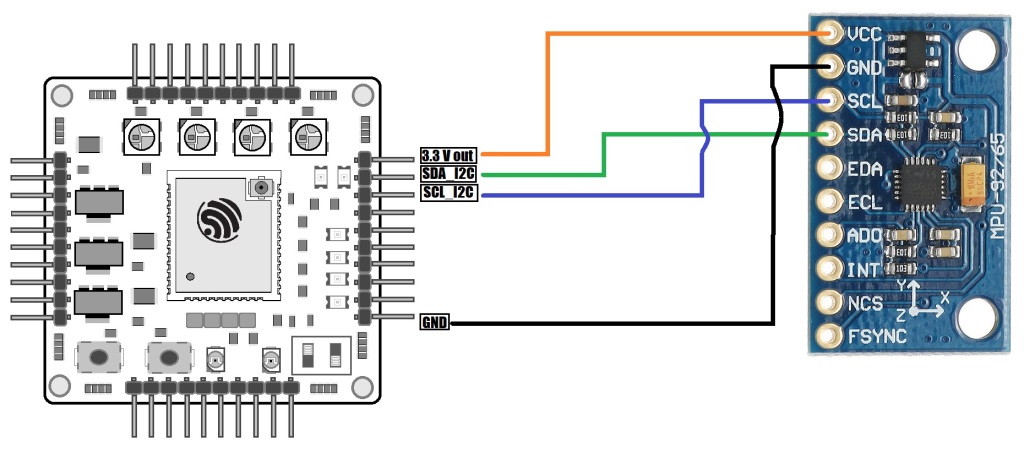
IMU – MPU9250 sensor.
Support calculation and export of calibrated values and filter noise with Extended Kalman Filter algorithm. Export IMU data in Real time.
Along with that, IMU-Viewer and Calibration Helper tools on Web Configure make simulation, test and calibration be more simple and intuitive .
(More circuit diagram, click here)
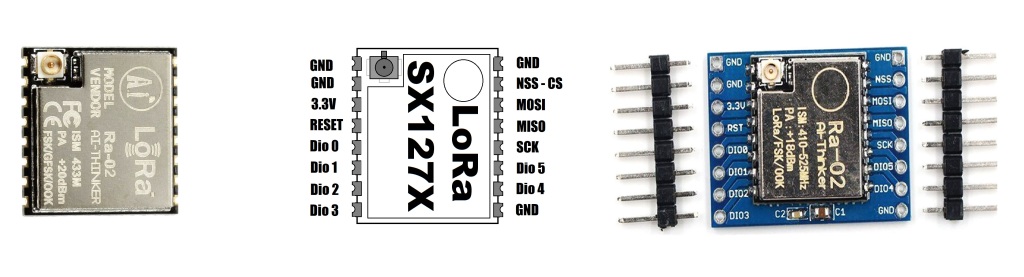
Radio - LoRa.
(More circuit diagram, click here)
When the internet connection is unavailable (the NTRIP / MQTT online service is not available), ESPrtk can use its WiFi signal to transmit GNSS data.
This is similar to the full MQTT functionality but is offline. The connections auto deployed in both protocols are TCP/UDP with the distance constrained to the WiFi transmit power.
ESPrtk will operate stably with a 400 to 500 meter baseline when using external antennas.
For LoRa link , ESPrtk 3.0.0 support communicate to external LoRa module (SX1276 , SX1277 , SX1278 , SX12769) via SPI port for km range stransmit.
Both support real-time data encryption / decryption using AES256.
| WIFI | LoRa | Unit | ||
Min | Max | Min | Max | ||
MAC /PHY | IEEE 80211 | LoRa | - | ||
Protocol | UDP/TCP-ESPrtk TM | LoRaTM - ESPrtkTM | - | ||
AES256 Encrypt | Yes | Yes |
| ||
2 ways transmit | Yes | Yes |
| ||
Channel | 1 | 14 | 1 | 14 | - |
Frequency | 2.4 Ghz | 2.5 Ghz | 412 Mhz | 915 Mhz | - |
Transmit power | 2 | 20 | 2 | 27 | dBm |
Transmit power | 1.59 | 100 | 1.59 | 500 | mW |
Speed in the air | 55 | 400 | 0.15 | 22 | Kbps |
Transmit Range | - | 1 | - | 50 | km |
Bandwidth | 20 Mhz | 40 Mhz | 56 Khz | 500 Khz | - |
WIFI TCP/UDP sender.
Act as a side action running with the main action at the same time.
This feature allows sending data get on RX_UART_RTK port (RX_UART_1 or RX_UART_2) to TCP / UDP device over WIFI connection.
Doesn't matter the format of the UART data (NMEA / RTCM / UBX / SKYTRAQ / RAW ...).
It also supports sending real-time IMU data to TCP / UDP device as the same work of Bluetooth connection
Besides, the TCP / UDP device can also act as a HOST and send control commands to ESPrtk in the same way as using on the RX / TX UART_0 port.
(HOST can send command PING, GPIO control command, check ESPrtk current system error, send restart command or control ESPrtk switch to UART / WEB Configure mode, ..... ESPrtk will respond ACK data / NACK back to HOST over TCP / UDP connection).
Click here to read more about TCP/UDP WIFI feature.
Supports 6 different types of connection modes and protocols:
- 1. TCP Server AP.
- 2. TCP Server STA.
- 3. TCP Server Client.
- 4. UDP Server AP.
- 5. UDP Server STA.
- 6. UDP Server Client.
RTCM 3.x, RAW, NMEA are data types transmitted.
ESPrtk uses two ways to transmit data:
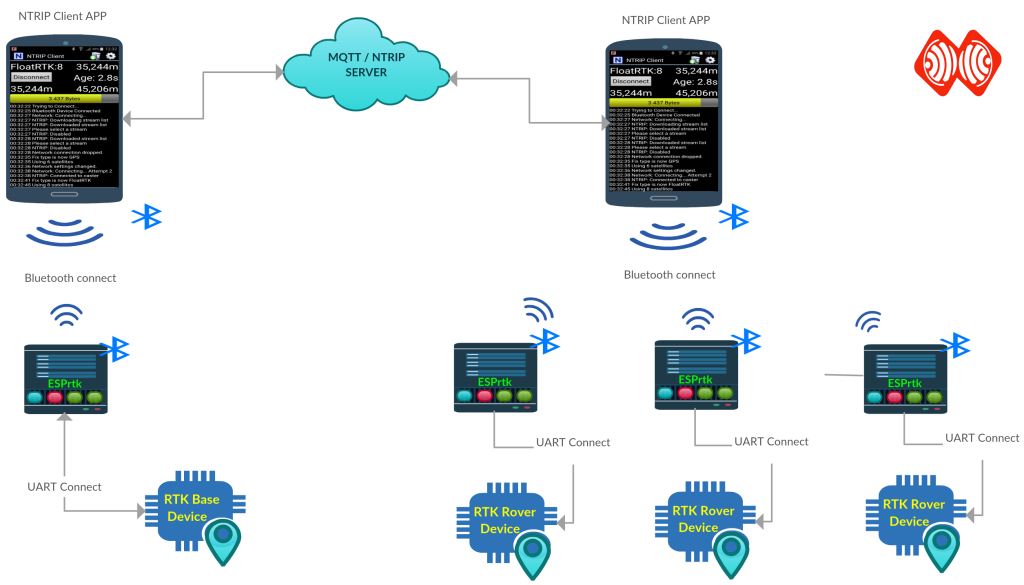
Online: ESPrtk is a client that uses a service to collect / distribute data from the server via an internet connection (WiFi/Ethernet).
Offline: ESPrtk will use its own Wifi or Bluetooth connection to perform wireless communication in the distribution of data.
If set to a Base, it will collect data from one of the UART ports and then send it over the wireless interface to one or more other devices (Rover).
If set to Rover, the data received from the Base will be streamed to the UART port to the RTK module.
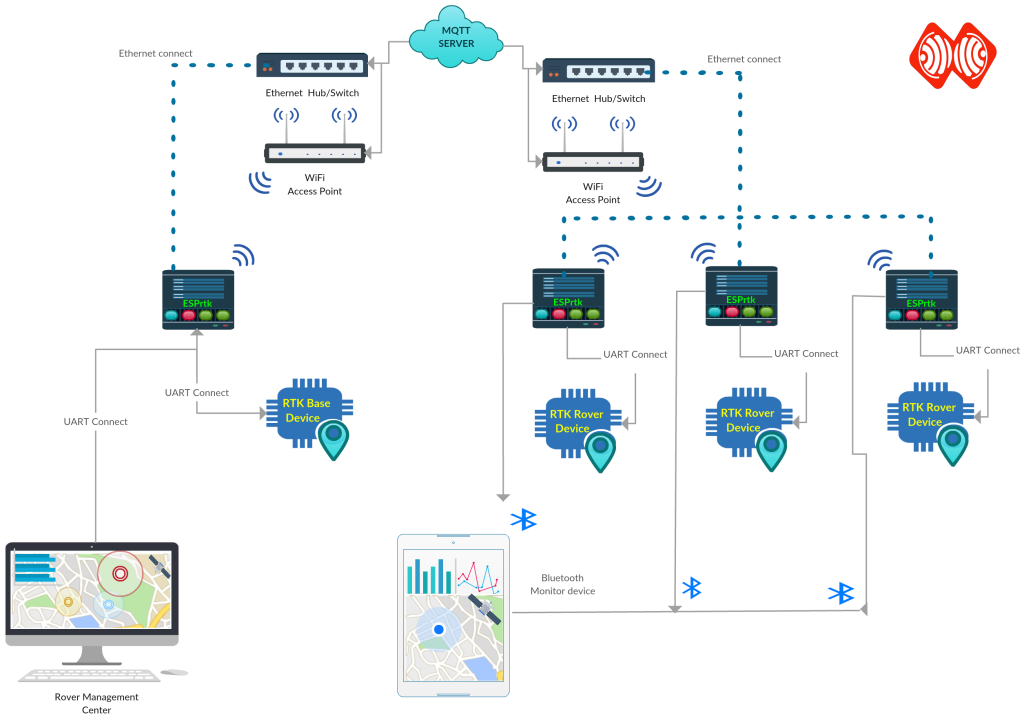
Run MQTT:
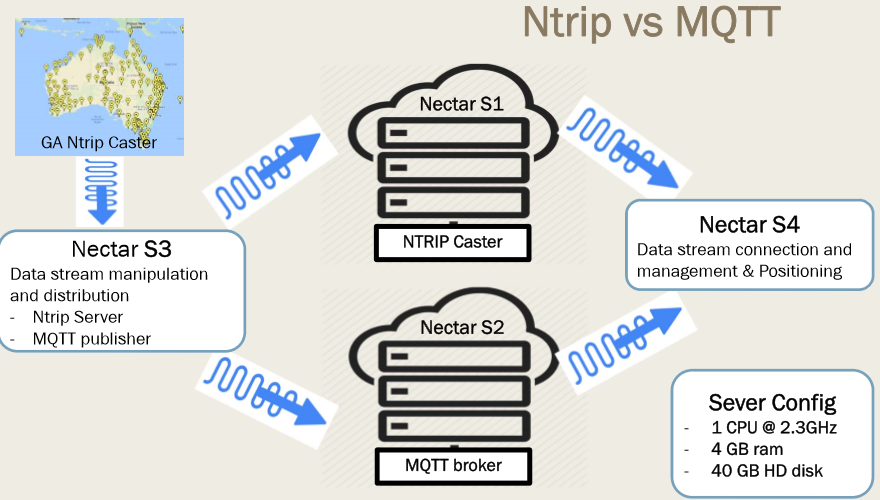
MQTT RTK is the most powerful transmission model today and will be the future alternative to NTRIP.
|
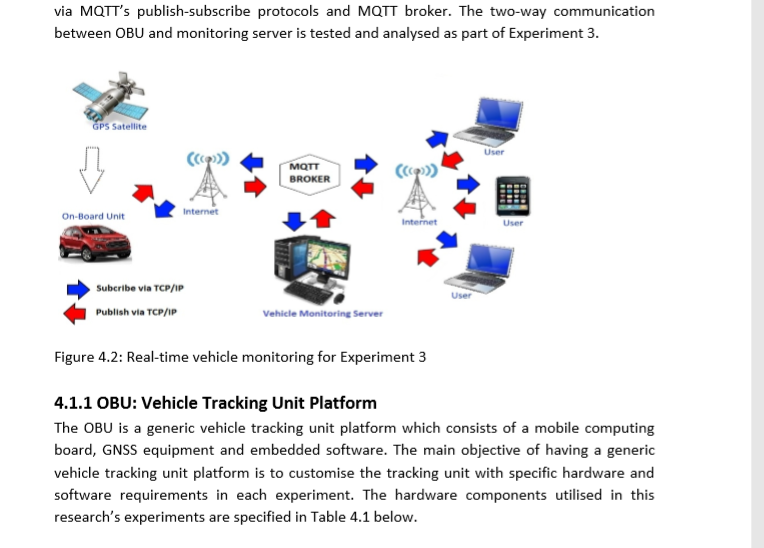
REAL-TIME VEHICLE MONITORING AND POSITIONING USING MQTT FOR RELIABLE WIRELESS CONNECTIVITY |
|
MQTT Protocol for Real‐Time GNSS Data |
|
China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC) 2018 Proceedings |
ESPrtk, when fully configured, can provide multiple connections at the same time.
ESPrtk is a Base can send RTCM / RAW to MQTT Server (Broker). (and Stream out NMEA data collection from the Rover to controler center.)
ESPrtk is a Rover that receives RTCM data from the Broker. ( can also export NMEA data to another device via Bluetooth at the same time ,or send back NMEA-$GGA to MQTT server at the sametime)
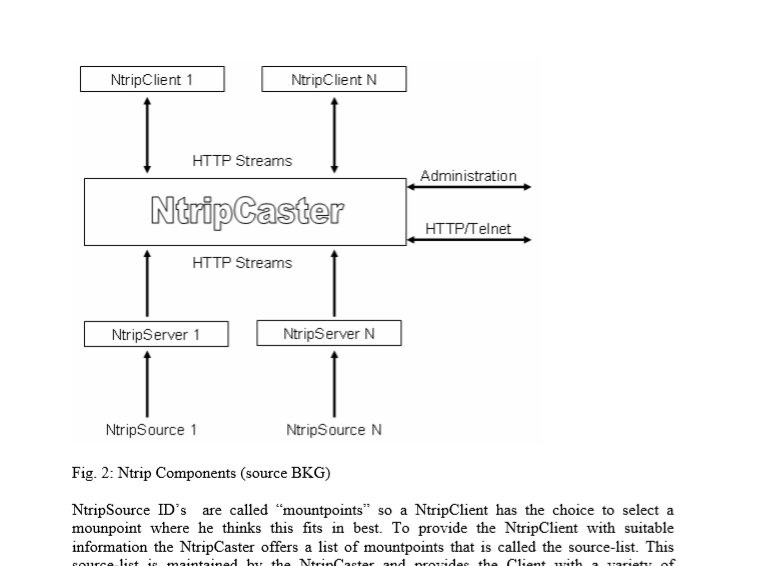
Run NTRIP:
NTRIP has a history of over 20 years of development with extensive base networks around the world. Supported on any existing device. ESPrtk too.
|
Networked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol (NTRIP) – Application and Benefit in Modern Surveying Systems |
|
INTRODUCTION TO GNSS NETWORK RTK-BAKU (AZERBAIDJAN) |
ESPrtk is a Base can send RTCM / RAW to NTRIP Server (Caster).
ESPrtk is a Rover that receives RTCM data from the Caster. ( can also export NMEA data to another device via Bluetooth at the same time or send back NMEA-$GGA to NTRIP server at the same time)
Offline using WiFi signal:
When the internet connection is unavailable (the NTRIP / MQTT online service is not available), ESPrtk can use its WiFi signal to transmit GNSS data.
This is similar to the full MQTT functionality but is offline. The connections deployed in both protocols are TCP and UDP with the distance constrained to the WiFi transmit power.
ESPrtk will operate stably with a 150 to 200 meter baseline when using external antennas.
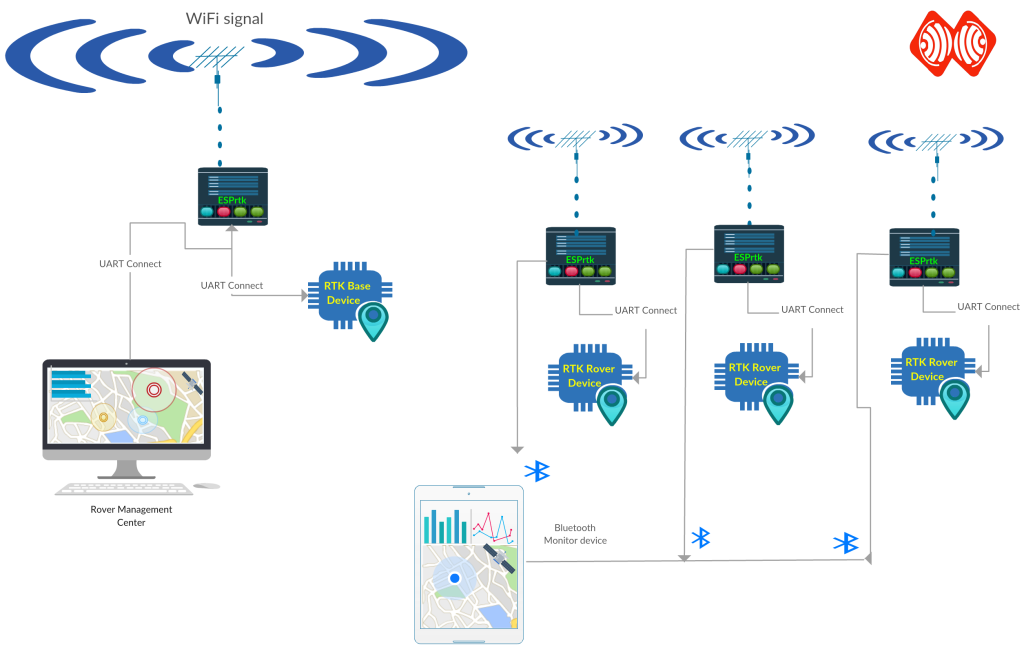
Bluetooth bridge RTK:
ESPrtk will work just like the Bluetooth-To-Serial module. It will collect (regardless of RTCM / NMEA / RAW / .. data type) from the RX-UART1 port and then send it to the Bluetooth device, or (and) Stream the data received via Bluetooth to the TX-UART2 port.
This function is particularly useful for users who want to collect output data from a GNSS device without having to directly connect to the wire. Featured Android applications such as “NTRIP Client” , “GNSS Surveyor”, “Bluetooth GPS”, “Bluetooth GPS Provider” ,”Mapit GIS”,”Bluetooth GPS Status Tool”, “SkyPro GPS Status Tool”…. supported this function.
(screenshot on GNSS Surveyor app)
And more…
There is much to say about detail ESPrtk with interesting functions on it. Hope the introduction is not too short to finish, please read other articles to know more about them..
So lets start create for your own ESPrtk board and use it, click here : How to use ESPrtk for your work and things need to know.
ESPrtk is a small circuit board used to transmit wireless GNSS data in high precision positioning applications.
ESPrtk is geared towards the ability to use high quality, independent, wireless and low cost platforms.
ESPrtk’s heart is a powerful ESP32 processor.
What does ESPrtk include?
ESPrtk is an abbreviation for ESP32 RTK.
ESPrtk is available in two formats. Software for DIY users and hardware for direct users.
ESPrtk can be used with many GNSS RTK devices.
RTK-capable receivers require precisely calibrated antennas to process signals transmitted by the GNSS satellites. The process for achieving centimeter-level position accuracy in GNSS involves a complex algorithm known as real time kinematic (RTK) processing. In addition, they must receive and process corrections data from a ground network of GNSS receivers. These factors made traditional RTK-capable receivers costly (in excess of $5000 or even $10,000 ) and bulky, making them unsuitable for cost- and size-sensitive applications.
Recently, GNSS equipment manufacturers have started advertising inexpensive (less than $500) and compact RTK-capable receivers. Some prominent names:
- Hemisphere- Eclipse P307 (L1/L2).
- NVS Technologies- NV08C-RTK (L1).
- Swift – Piksi Multi (L1/L2).
- u-blox -NEO-M8P (L1).
- Skytraq -S2525F8 (L1).
|
Evaluation of Low-Cost, Centimeter-Level Accuracy OEM GNSS Receivers. |
RTK receivers are getting smaller and smaller, but accuracy is improving. At the same time, there was a powerful embedded CHIP is ESP32, which attracted everyone in IoT applications and GNSS data transmission for RTK positioning is one of them.
This is the best time to promote RTK.
ESPrtk aims to be simple, user-friendly and safe to use.
ESPrtk was born to provide High quality RTK positioning solution with low cost option. This is an effort to make accessing and using high-precision positioning technology easier for everyone. Especially for those who have hobby about it.
Wired connections for extremely simple use will make things faster.
(More circuit diagram, click here)
Highlights of the design are the Web Config User Interface (UI) application, which makes it easy to test or configure it and the peripherals it connects to.
Along with that are layers of security with high-level encryption for transmitting GNSS data to public servers (where your data can be abused without your permission). Data encryption is also applied to all important files on ESPrtk in order to protect users as much as possible. Users can even activate a permanent lock with their password to make sure no one can change anything on their ESPrtk.
(More circuit diagram, click here)
Support Bluetooth ,WIFI and Ethernet connection.
You do not need to purchase HC05 module for wireless connections, ESPrtk also supports bluetooth and can use it in “UART + Bluetooth 2 ways bridge (Transmiter + Receiver)“ mode with just one quick setting.
High-speed wireless WIFI connection on ESP32 helps mobile connections for flexible Rover devices.
Ethernet connection will be suitable for Basestation with absolute stability.
Both of them are supported on ESPrtk.
Ethernet module support is ENC28J60 , communicate to ESPrtk via SPI port to access internet.
(More circuit diagram, click here)
U-Center and GNSSViewer inside.
Well, you don’t need to bring your computer to configure Ublox modules or Navspark either because both of these functions have been integrated on the WEB Configure of ESPrtk. They are also designed with the same interface as the original version of U-Center and GNSSViewer to bring a feeling similar to when using software on a computer.
Both of these functions are supported with full of important features and the latest protocol for modules such as M8P, F9P, LEA, NEO .. of Ublox and NS-HP-xx, INS 3D, .. of Navspark.
(More circuit diagram, click here)
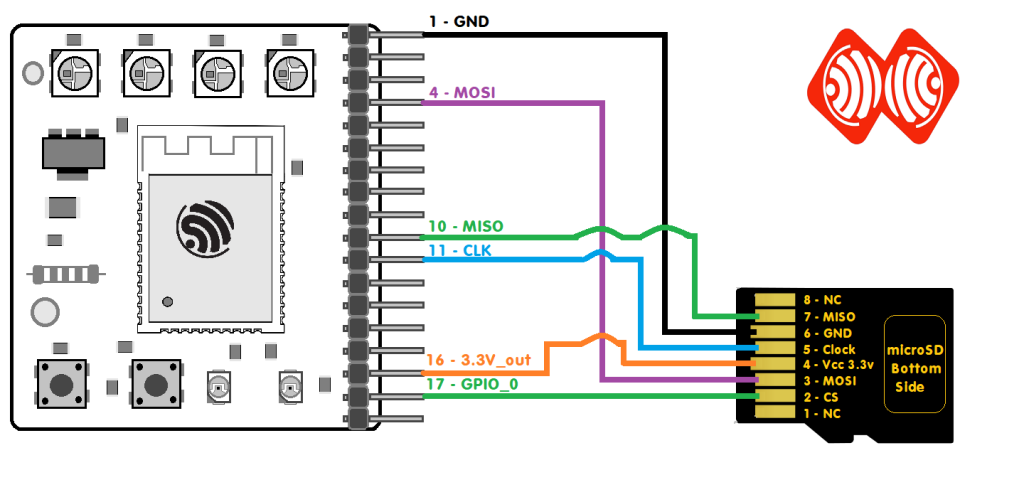
SD Card to Log NMEA/RTCM data.
When activated, ESPrtk will collect NMEA sentences from RX_UART1 port and save it to the SD card as a text file (or log file). Users can then use those files for surveying and evaluating positioning.
NMEA Logger on ESPrtk supports a variety of file formats, update cycles, NMEA filters, recording styles, etc.
This function is integrated on the Rover (Client) and all connections such as NTRIP – MQTT – WIFI TCP-WIFI UDP.
(More circuit diagram, click here)
OLED Display or Neopixel Strip.
Besides displaying status by Neopixel and LED.
Since 2.7.0 ESPrtk OLED has been integrated to provide more information and operational status of ESPrtk.
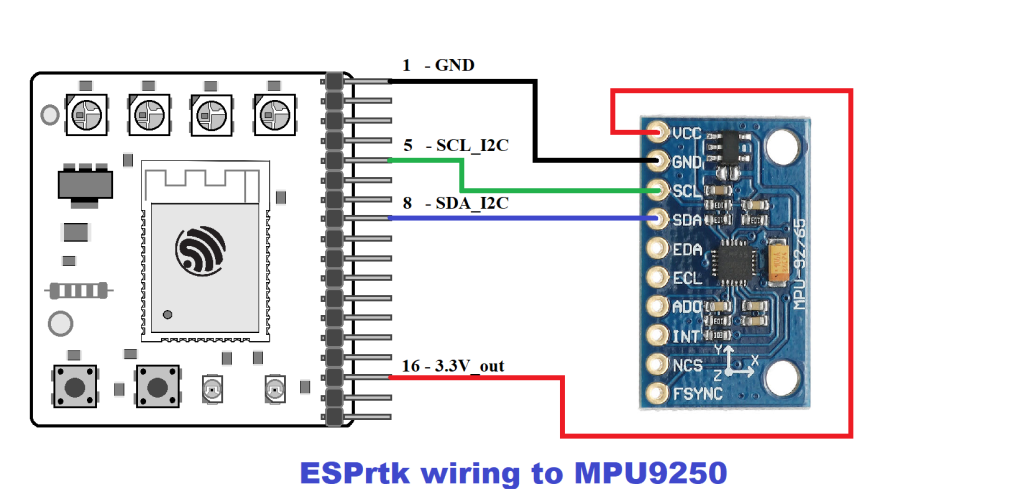
IMU – MPU9250 sensor.
Support calculation and export of calibrated values and filter noise with Extended Kalman Filter algorithm. Export IMU data in Real time.
Along with that, IMU-Viewer and Calibration Helper tools on Web Configure make simulation, test and calibration be more simple and intuitive .
(More circuit diagram, click here)
Radio - LoRa.
(More circuit diagram, click here)
When the internet connection is unavailable (the NTRIP / MQTT online service is not available), ESPrtk can use its WiFi signal to transmit GNSS data.
This is similar to the full MQTT functionality but is offline. The connections auto deployed in both protocols are TCP/UDP with the distance constrained to the WiFi transmit power.
ESPrtk will operate stably with a 400 to 500 meter baseline when using external antennas.
For LoRa link , ESPrtk 3.0.0 support communicate to external LoRa module (SX1276 , SX1277 , SX1278 , SX12769) via SPI port for km range stransmit.
Both support real-time data encryption / decryption using AES256.
| WIFI | LoRa | Unit | ||
Min | Max | Min | Max | ||
MAC /PHY | IEEE 80211 | LoRa | - | ||
Protocol | UDP/TCP-ESPrtk TM | LoRaTM - ESPrtkTM | - | ||
AES256 Encrypt | Yes | Yes |
| ||
2 ways transmit | Yes | Yes |
| ||
Channel | 1 | 14 | 1 | 14 | - |
Frequency | 2.4 Ghz | 2.5 Ghz | 412 Mhz | 915 Mhz | - |
Transmit power | 2 | 20 | 2 | 27 | dBm |
Transmit power | 1.59 | 100 | 1.59 | 500 | mW |
Speed in the air | 55 | 400 | 0.15 | 22 | Kbps |
Transmit Range | - | 1 | - | 50 | km |
Bandwidth | 20 Mhz | 40 Mhz | 56 Khz | 500 Khz | - |
RTCM 3.x, RAW, NMEA are data types transmitted.
ESPrtk uses two ways to transmit data:
Online: ESPrtk is a client that uses a service to collect / distribute data from the server via an internet connection (WiFi/Ethernet).
Offline: ESPrtk will use its own Wifi or Bluetooth connection to perform wireless communication in the distribution of data.
If set to a Base, it will collect data from one of the UART ports and then send it over the wireless interface to one or more other devices (Rover).
If set to Rover, the data received from the Base will be streamed to the UART port to the RTK module.
Run MQTT:
MQTT RTK is the most powerful transmission model today and will be the future alternative to NTRIP.
|
REAL-TIME VEHICLE MONITORING AND POSITIONING USING MQTT FOR RELIABLE WIRELESS CONNECTIVITY |
|
MQTT Protocol for Real‐Time GNSS Data |
|
China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC) 2018 Proceedings |
ESPrtk, when fully configured, can provide multiple connections at the same time.
ESPrtk is a Base can send RTCM / RAW to MQTT Server (Broker). (and Stream out NMEA data collection from the Rover to controler center.)
ESPrtk is a Rover that receives RTCM data from the Broker. ( can also export NMEA data to another device via Bluetooth at the same time ,or send back NMEA-$GGA to MQTT server at the sametime)
Run NTRIP:
NTRIP has a history of over 20 years of development with extensive base networks around the world. Supported on any existing device. ESPrtk too.
|
Networked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol (NTRIP) – Application and Benefit in Modern Surveying Systems |
|
INTRODUCTION TO GNSS NETWORK RTK-BAKU (AZERBAIDJAN) |
ESPrtk is a Base can send RTCM / RAW to NTRIP Server (Caster).
ESPrtk is a Rover that receives RTCM data from the Caster. ( can also export NMEA data to another device via Bluetooth at the same time or send back NMEA-$GGA to NTRIP server at the same time)
Offline using WiFi signal:
When the internet connection is unavailable (the NTRIP / MQTT online service is not available), ESPrtk can use its WiFi signal to transmit GNSS data.
This is similar to the full MQTT functionality but is offline. The connections deployed in both protocols are TCP and UDP with the distance constrained to the WiFi transmit power.
ESPrtk will operate stably with a 150 to 200 meter baseline when using external antennas.
Bluetooth bridge RTK:
ESPrtk will work just like the Bluetooth-To-Serial module. It will collect (regardless of RTCM / NMEA / RAW / .. data type) from the RX-UART1 port and then send it to the Bluetooth device, or (and) Stream the data received via Bluetooth to the TX-UART2 port.
This function is particularly useful for users who want to collect output data from a GNSS device without having to directly connect to the wire. Featured Android applications such as “NTRIP Client” , “GNSS Surveyor”, “Bluetooth GPS”, “Bluetooth GPS Provider” ,”Mapit GIS”,”Bluetooth GPS Status Tool”, “SkyPro GPS Status Tool”…. supported this function.
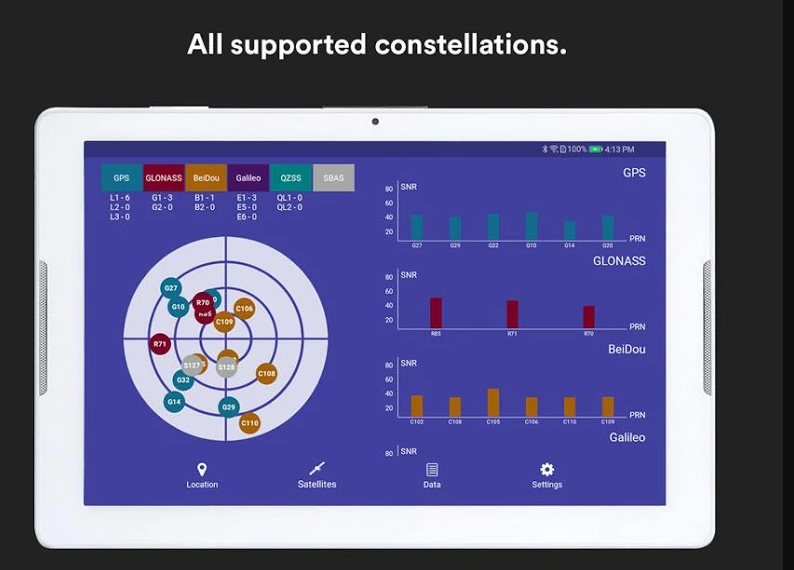
(screenshot on GNSS Surveyor app)
And more…
There is much to say about detail ESPrtk with interesting functions on it. Hope the introduction is not too short to finish, please read other articles to know more about them..
So lets start create for your own ESPrtk board and use it, click here : How to use ESPrtk for your work and things need to know.
ESPrtk is a small circuit board used to transmit wireless GNSS data in high precision positioning applications.
ESPrtk is geared towards the ability to use high quality, independent, wireless and low cost platforms.
ESPrtk’s heart is a powerful ESP32 processor.
What does ESPrtk include?
ESPrtk is an abbreviation for ESP32 RTK.
ESPrtk is available in two formats. Software for DIY users and hardware for direct users.
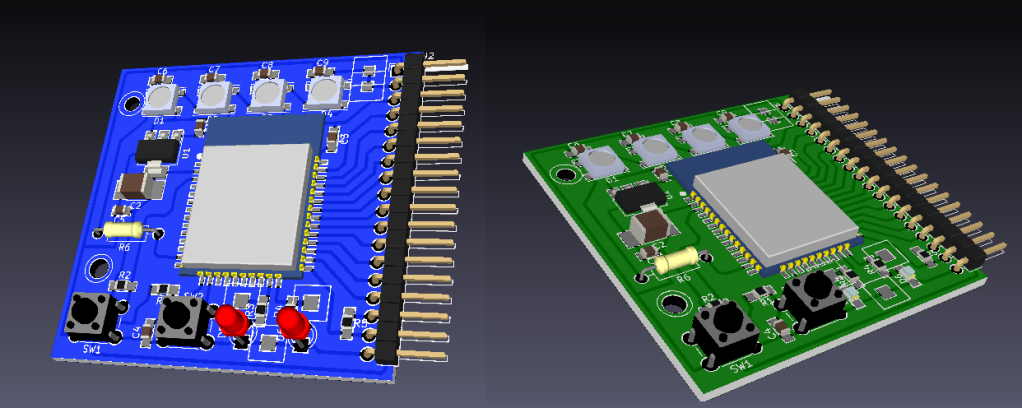
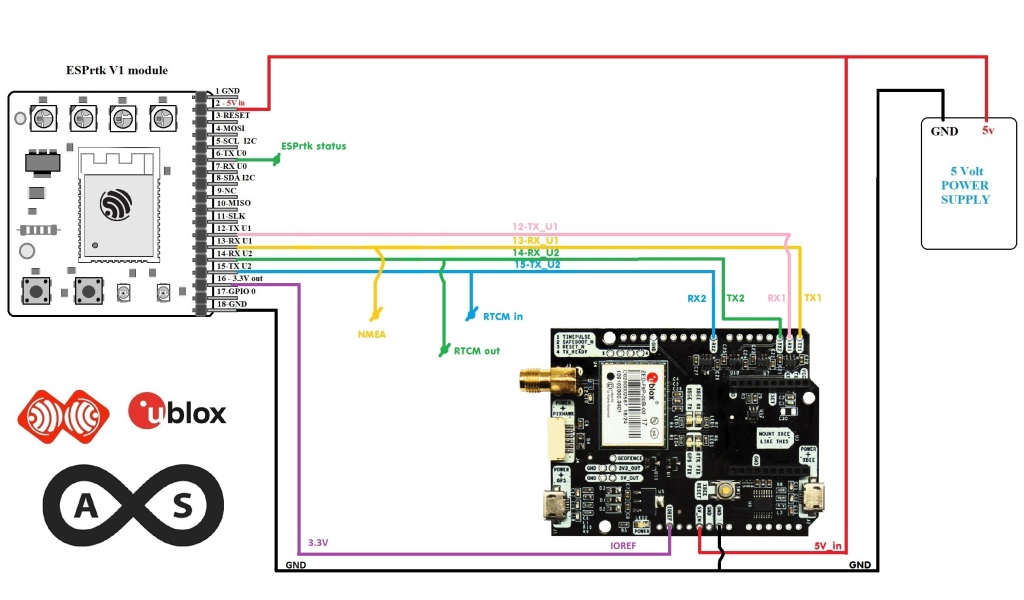
An ESPrtk V1 circuit board:
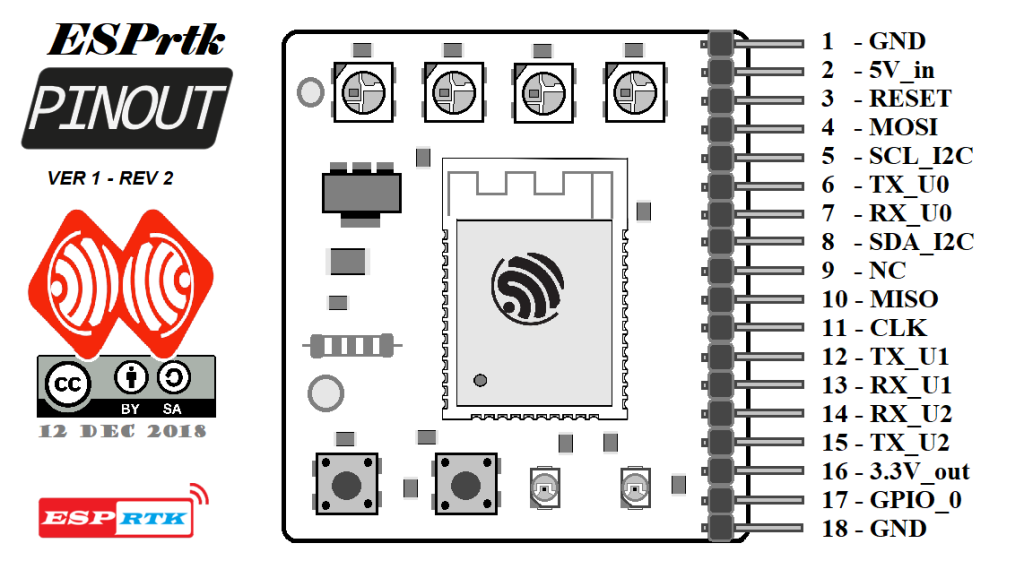
ESPrtk board V.1 pinout
In 2.7.5 version , it support :
- Web config:
- RTK Linking:
- NTRIP (Client/Server/ Client send back NMEA/ Client BLE).
- MQTT (Client/Master/ Client send back NMEA/ Client BLE).
- Wifi-TCP (Client/Master/ Client send back NMEA/ Client BLE).
- Wifi-UDP (Master/ Client send back NMEA/ Client BLE)……
- Bluetooth to Serial.(Client/Server)
- Internet :
- Wifi.
- Ethernet LAN ENC28J60…..
- Display: OLED , Neopixel, Led….
- Custom pinmap .
- SD Card :
- IMU-MPU9250 sensor: Export IMU data in real time , Calibration Helper , IMU Viewer,…
ESPrtk can be used with many GNSS RTK devices.
RTK-capable receivers require precisely calibrated antennas to process signals transmitted by the GNSS satellites. The process for achieving centimeter-level position accuracy in GNSS involves a complex algorithm known as real time kinematic (RTK) processing. In addition, they must receive and process corrections data from a ground network of GNSS receivers. These factors made traditional RTK-capable receivers costly (in excess of $5000 or even $10,000 ) and bulky, making them unsuitable for cost- and size-sensitive applications.
Recently, GNSS equipment manufacturers have started advertising inexpensive (less than $500) and compact RTK-capable receivers. Some prominent names:
- Hemisphere- Eclipse P307 (L1/L2).
- NVS Technologies- NV08C-RTK (L1).
- Swift – Piksi Multi (L1/L2).
- u-blox -NEO-M8P (L1).
- Skytraq -S2525F8 (L1).
|
Evaluation of Low-Cost, Centimeter-Level Accuracy OEM GNSS Receivers. |
RTK receivers are getting smaller and smaller, but accuracy is improving. At the same time, there was a powerful embedded CHIP is ESP32, which attracted everyone in IoT applications and GNSS data transmission for RTK positioning is one of them.
This is the best time to promote RTK.
ESPrtk aims to be simple, user-friendly and safe to use.
ESPrtk was born to provide High quality RTK positioning solution with low cost option. This is an effort to make accessing and using high-precision positioning technology easier for everyone. Especially for those who have hobby about it.
Wired connections for extremely simple use will make things faster.
Highlights of the design are the Web Config User Interface (UI) application, which makes it easy to test or configure it and the peripherals it connects to.
Along with that are layers of security with high-level encryption for transmitting GNSS data to public servers (where your data can be abused without your permission). Data encryption is also applied to all important files on ESPrtk in order to protect users as much as possible. Users can even activate a permanent lock with their password to make sure no one can change anything on their ESPrtk.
Support Bluetooth ,WIFI and Ethernet connection.
You do not need to purchase HC05 module for wireless connections, ESPrtk also supports bluetooth and can use it in “Bluetooth to Serial“ mode with just one quick setting.
High-speed wireless WIFI connection on ESP32 helps mobile connections for flexible Rover devices.
Ethernet connection will be suitable for Basestation with absolute stability.
Both of them are supported on ESPrtk.
Ethernet module support is ENC28J60 , communicate to ESPrtk via SPI port to access internet.
U-Center and GNSSViewer inside.
Well, you don’t need to bring your computer to configure Ublox modules or Navspark either because both of these functions have been integrated on the WEB Configure of ESPrtk. They are also designed with the same interface as the original version of U-Center and GNSSViewer to bring a feeling similar to when using software on a computer.
Both of these functions are supported with full of important features and the latest protocol for modules such as M8P, F9P, LEA, NEO .. of Ublox and NS-HP-xx, INS 3D, .. of Navspark.
SD Card to Log NMEA/RTCM data.
When activated, ESPrtk will collect NMEA sentences from RX_UART1 port and save it to the SD card as a text file (or log file). Users can then use those files for surveying and evaluating positioning.
NMEA Logger on ESPrtk supports a variety of file formats, update cycles, NMEA filters, recording styles, etc.
This function is integrated on the Rover (Client) and all connections such as NTRIP – MQTT – WIFI TCP-WIFI UDP.
OLED Display or Neopixel Strip.
Besides displaying status by Neopixel and LED.
Since 2.7.0 ESPrtk OLED has been integrated to provide more information and operational status of ESPrtk.
IMU – MPU9250 sensor.
The lastest function added to version 2.7.5.
Support calculation and export of calibrated values and filter noise with Extended Kalman Filter algorithm. Export IMU data in Real time.
Along with that, IMU-Viewer and Calibration Helper tools on Web Configure make simulation, test and calibration be more simple and intuitive .
RTCM 3.x, RAW, NMEA are data types transmitted.
ESPrtk uses two ways to transmit data:
Online: ESPrtk is a client that uses a service to collect / distribute data from the server via an internet connection (WiFi/Ethernet).
Offline: ESPrtk will use its own Wifi or Bluetooth connection to perform wireless communication in the distribution of data.
If set to a Base, it will collect data from one of the UART ports and then send it over the wireless interface to one or more other devices (Rover).
If set to Rover, the data received from the Base will be streamed to the UART port to the RTK module.
Run MQTT:
MQTT RTK is the most powerful transmission model today and will be the future alternative to NTRIP.
|
REAL-TIME VEHICLE MONITORING AND POSITIONING USING MQTT FOR RELIABLE WIRELESS CONNECTIVITY |
|
MQTT Protocol for Real‐Time GNSS Data |
|
China Satellite Navigation Conference (CSNC) 2018 Proceedings |
ESPrtk, when fully configured, can provide multiple connections at the same time.
ESPrtk is a Base can send RTCM / RAW to MQTT Server (Broker). (and Stream out NMEA data collection from the Rover to controler center.)
ESPrtk is a Rover that receives RTCM data from the Broker. ( can also export NMEA data to another device via Bluetooth at the same time ,or send back NMEA-$GGA to MQTT server at the sametime)
Run NTRIP:
NTRIP has a history of over 20 years of development with extensive base networks around the world. Supported on any existing device. ESPrtk too.
|
Networked Transport of RTCM via Internet Protocol (NTRIP) – Application and Benefit in Modern Surveying Systems |
|
INTRODUCTION TO GNSS NETWORK RTK-BAKU (AZERBAIDJAN) |
ESPrtk is a Base can send RTCM / RAW to NTRIP Server (Caster).
ESPrtk is a Rover that receives RTCM data from the Caster. ( can also export NMEA data to another device via Bluetooth at the same time or send back NMEA-$GGA to NTRIP server at the same time)
Offline using WiFi signal:
When the internet connection is unavailable (the NTRIP / MQTT online service is not available), ESPrtk can use its WiFi signal to transmit GNSS data.
This is similar to the full MQTT functionality but is offline. The connections deployed in both protocols are TCP and UDP with the distance constrained to the WiFi transmit power.
ESPrtk will operate stably with a 150 to 200 meter baseline when using external antennas.
Bluetooth bridge RTK:
ESPrtk will work just like the Bluetooth-To-Serial module. It will collect (regardless of RTCM / NMEA / RAW / .. data type) from the RX-UART1 port and then send it to the Bluetooth device, or (and) Stream the data received via Bluetooth to the TX-UART2 port.
This function is particularly useful for users who want to collect output data from a GNSS device without having to directly connect to the wire. Featured Android applications such as “NTRIP Client” , “GNSS Surveyor”, “Bluetooth GPS”, “Bluetooth GPS Provider” ,”Mapit GIS”,”Bluetooth GPS Status Tool”, “SkyPro GPS Status Tool”…. supported this function.
(screenshot on GNSS Surveyor app)
And more…
There is much to say about detail ESPrtk with interesting functions on it. Hope the introduction is not too short to finish, please read other articles to know more about them..
So lets start create for your own ESPrtk board and use it, click here : How to use ESPrtk for your work and things need to know.